What Is a Tankless Water Heater? Things You Need to Know!
If you’ve ever wondered, “What is a tankless water heater?” you’re not alone. Many homeowners today are exploring more energy-efficient and eco-friendly solutions for their hot water needs, and tankless water heaters stand out as a promising option.
In this article, we’ll present some details of what tankless water heaters are, how they work, and why they might be the right choice for your home. We’ll explore their innovative design and cover the key components that make these heaters efficient and reliable.

What Is a Tankless Water Heater?
Tankless water heaters, also known as on-demand or instant systems, heat water only when you need it, without the standby energy losses associated with traditional tank systems.
They heat water directly as it flows through the heat exchanger, providing a continuous supply and significant energy savings.
These benefits are making them an increasingly popular choice for eco-conscious homeowners and those looking to upgrade their home’s efficiency. Compact and efficient, these models are ideal for homes both small and large that prioritize energy efficiency, a smaller footprint, and convenience.
How Does a Tankless Water Heater Work?
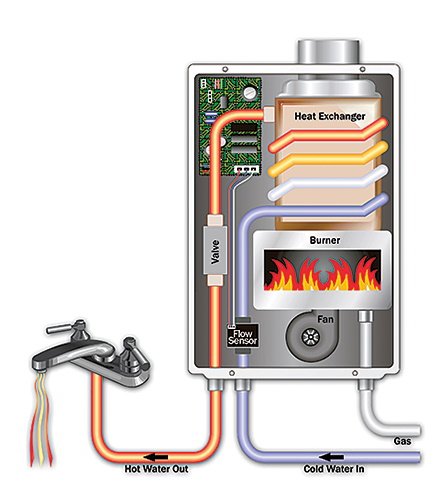
Tankless water heaters operate under a simple yet effective principle: they heat water directly as it flows through the device, avoiding the need to store pre-heated water. When you turn on a hot water tap in your home, the unit detects the water flow. This triggers a water flow sensor within the heater, which then signals the control system to start heating the water.
In the case of gas-powered tankless water heaters, the control system triggers the gas burner to ignite, usually through an electronic ignition system, meaning there is no continuously burning pilot light, which enhances the system’s efficiency.
As the burner ignites, it heats the water passing through a heat exchanger. The heat exchanger is essentially a series of coils or a panel that the water flows through, gaining heat from the hot gases produced by the burner. The design of the heat exchanger ensures that the water is heated quickly and efficiently.
In non-condensing units, the hot gases that heat the water cool down as they transfer their heat and are then expelled outdoors through a vent. Condensing models take a different approach by passing these gases through a secondary heat exchanger. This process captures additional heat from the gases before they are vented, significantly boosting the unit’s efficiency.
Electric tankless heaters, alternatively, direct electricity to heating elements-similar to those found in electric kettles-once they detect water flow. The water flows over these elements, absorbing heat directly. A modulation system within the control panel controls the elements, adjusting the electricity flow to maintain consistent water temperatures and optimize energy use.
As long as the tap remains open, the system continues to detect water flow, maintaining the operation of the gas burner or electric elements and consistently heating the water. When the tap is closed, the flow sensor signals the burner to turn off, halting the heating process and conserving energy.
Detailed Components of Tankless Water Heaters
Heat Exchanger
The heart of a tankless water heater is its heat exchanger, which instantly heats the water as it passes through. Made from highly conductive materials such as copper or stainless steel, the heat exchanger rapidly transfers heat from the gas burner or electric coil to the water.
Secondary Heat Exchanger
In addition to the primary heat exchanger, condensing tankless water heaters also include a secondary heat exchanger that utilizes the heat from exhaust gases to further warm the incoming water. This process captures additional heat that would otherwise be lost, significantly enhancing the overall energy efficiency of the system.
Condensing models are particularly effective in colder climates or in larger households where the demand for hot water is higher, making them a more energy-efficient choice overall.
Water Flow Sensor
The water flow sensor plays a vital role by detecting the flow of water when a hot water tap is turned on, usually activating at flow rates as low as 0.3-0.5 gallons per minute (GPM). This sensor ensures that the heater operates only when necessary, thereby conserving energy.
Its precision prevents the unit from heating water when there is no demand, thereby avoiding unnecessary energy use and contributing to the overall energy efficiency of the home.
Control Panel
The control panel offers user-friendly interfaces that allow homeowners to adjust the water temperature to their preference, typically within a range of 100°F to 140°F. More advanced panels include diagnostics and error-reporting features, which play a critical role in maintaining the efficiency of the heater by allowing for quick troubleshooting and adjustments.
This capability not only ensures optimal operation but also helps in minimizing energy waste, as the temperature can be precisely controlled to avoid excess heating.
Electric Elements
In electric tankless water heaters, the electric elements are fundamental to the heating process. These elements, functioning like large resistors, heat up as electricity passes through them, directly heating the water that flows over them.
This method is particularly efficient because it transfers heat to the water immediately, ensuring that energy is used only when actually needed. This reduces the standby losses typically associated with traditional tank heaters.
Moreover, their high energy factor (EF) ratings, often up to 0.99, demonstrate their ability to convert a large portion of the electricity consumed directly into heat, making them an energy-efficient choice for heating water.
Gas Burner
For gas-powered models, the gas burner is the core heating component. When activated by the water flow sensor, the burner ignites to heat the water passing through the heat exchanger.
Non-condensing gas tankless water heaters typically operate with an energy efficiency of around 80% to 85%, as they exhaust a portion of the heat as waste gases.
In contrast, condensing units can achieve higher efficiencies, usually between 90% to 98%, by utilizing a secondary heat exchanger to capture and recycle heat from exhaust gases before they are vented out. This allows them to make better use of the energy consumed and reduce overall energy costs.
Exhaust Vent
Gas models also incorporate an exhaust vent, which is essential for safely directing combustion gases out of the home. This system not only ensures the safety and efficiency of the heater but also helps in maintaining good air quality within the residence.
Blower Fan
Included as part of the venting system in gas tankless water heaters, the blower fan plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe operation of the unit. It helps expel combustion gases through the vent, making sure they don’t linger in your home.
This component is particularly important in tightly sealed homes where proper venting is critical for maintaining indoor air quality and preventing potential hazards associated with gas appliances.
Modulating Gas Valve
The modulating gas valve is a key feature in many modern tankless water heaters, allowing the unit to precisely control the amount of gas flowing to the burner.
This smart component adjusts the flame size based on real-time water demand, which means it uses just enough energy to heat the water you’re using, rather than heating at full blast all the time. This not only enhances the efficiency of the heater but also extends its lifespan by preventing overuse.
Modulation in Electric Tankless Water Heaters
Some electric tankless water heaters are also designed with modulation, adjusting the power output to the heating elements based on real-time hot water demand. This system activates when a hot water tap is opened, and the flow sensor within the heater detects water movement, prompting the control system to calculate the necessary energy to reach the user-set temperature.
This calculation takes into account the incoming water temperature and flow rate. Depending on the demand, the control panel either increases or decreases the electrical current to the elements, ensuring only the required amount of energy is used.
Ignition Electrodes
Ignition electrodes are vital for the safe and efficient operation of gas tankless water heaters. These electrodes spark to ignite the gas as soon as the water flow is detected, ensuring that the heater starts heating water without delay.
Their reliability and quick response are essential for providing immediate hot water and for the overall energy efficiency of the system, as they eliminate the need for a pilot light that burns gas continuously.
Advanced Electronics
Advanced electronics in tankless water heaters, such as WiFi connectivity and compatibility with smart home assistants like Alexa, are changing the way we manage our home heating systems. These features allow you to control the temperature and monitor energy usage from your smartphone or through voice commands, offering a convenient, high-tech way to optimize your home’s energy consumption and comfort.
For instance, some systems can even alert you to maintenance needs or efficiency issues, helping you keep the unit running smoothly without surprises.
Recirculation Systems
Some high-end models, like those from Rinnai, come equipped with a built-in recirculation system that provides hot water more quickly and reduces water waste.
This system keeps hot water circulating through the pipes, so it’s available on demand without the wait, perfect for larger homes or for those who are environmentally conscious and looking to save on water usage. It’s a game changer in how we access hot water, blending convenience with sustainability.
Safety Features
Safety features in tankless water heaters are comprehensive and designed to protect your home from any potential risks associated with water heating. These include overheat sensors that shut down the heater if water temperatures exceed safe levels, freeze protection systems that prevent the unit and the pipes from freezing in cold weather, and exhaust and water flow sensors that ensure everything is operating safely. These built-in protections make tankless water heaters not just more efficient but significantly safer for daily use.
Conclusion
Tankless water heaters represent a significant advancement in heating technology, offering efficient, reliable, and continuous hot water.
By understanding what a tankless water heater is, how it works, the components involved, and the benefits, homeowners can make informed decisions about upgrading their water heating systems to align with modern standards of efficiency and convenience.
With their compact design and capability to reduce energy waste, tankless heaters are an excellent choice for modernizing home water heating systems, providing both immediate and long-term benefits.
More About Water Heating

What Is: Power Vent Water Heaters (Including Pros and Cons)
Power vent water heaters offer flexibility and efficiency, making them a standout choice among the many options available for home…

What Is: Direct Vent Water Heater (With Pros and Cons)
When you’re considering a new water heater for your home, the myriad of options can quickly become overwhelming, including atmospheric,…

What Is: Energy Factor (EF) and Uniform Energy Factor (UEF) in Water Heaters
When you’re in the market for a new water heater, you might come across two important metrics: Energy Factor (EF)…