Heat Pumps vs. Gas Furnaces: Which HVAC System is Better?
When it comes to the debate of heat pumps vs. gas furnaces, choosing the right heating system for your home can feel like navigating a maze of options. If you’re thinking about a new HVAC system and want to compare these two popular choices, the process can be confusing and time-consuming. That’s why we’ve made it easy to understand.
This guide aims to simplify that task by comparing air-to-air heat pumps and gas furnaces, highlighting their unique benefits and challenges. By understanding the key factors involved, you can make an informed decision that ensures comfort, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.


Exploring Heat Pumps
How Heat Pumps Work
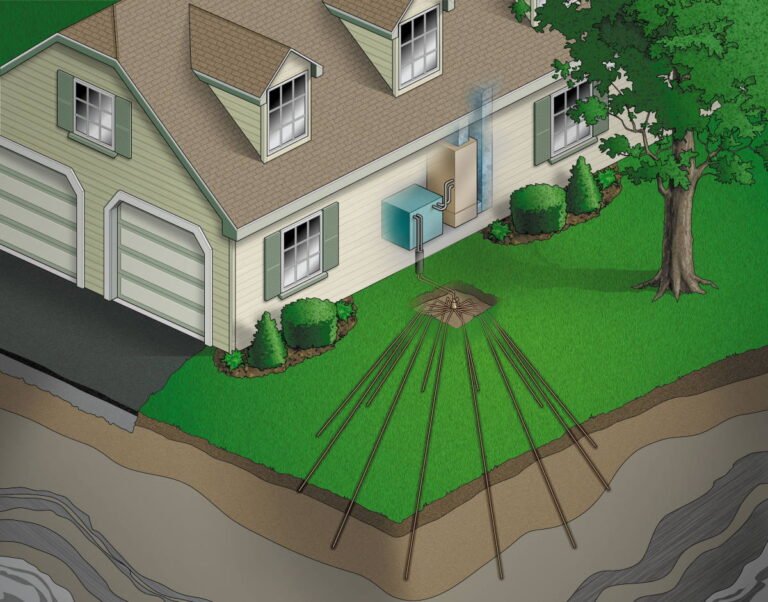
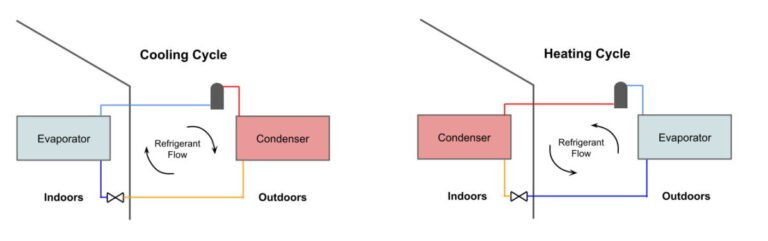
Heat pumps operate on a principle similar to that of a refrigerator, transferring heat from one place to another rather than generating it.
They use a refrigerant to absorb heat from the outside air, ground, or water and then compress it to increase its temperature. This heat is then transferred into your home through a heat exchanger.
In cooling mode, the process is reversed: the heat pump extracts heat from the indoor air and releases it outside, effectively cooling your home. This dual functionality makes heat pumps a versatile option for both heating and cooling needs, though their efficiency can decrease in extremely cold climates.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can reduce electricity use for heating by approximately 50% compared to electric resistance heating, making them an energy-efficient choice for moderate climates.
The Benefits of Home Heating with Heat Pumps
Energy Efficiency
Heat pumps are highly efficient because they transfer heat rather than generate it. They can achieve efficiencies of 300% to 400%, which means that for every unit of electricity consumed, they can transfer three to four units of heat energy. This can result in significantly lower energy bills compared to traditional heating systems, especially in milder climates. Modern high-efficiency gas furnaces have Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) ratings of 90% to 98%, meaning they convert 90% to 98% of the natural gas they consume into heat.
Dual Functionality
One of the standout benefits of heat pumps is their ability to serve as both a heating and cooling system. During the winter, they move heat into your home, and in the summer, they reverse the process to cool your home, eliminating the need for separate systems. They can also dehumidify the house, improving indoor air quality and comfort.
Environmentally Friendly
Heat pumps have a lower environmental impact since they rely on electricity rather than burning fossil fuels. However, homeowners should be aware that while they aren’t directly polluting, they are still involved in the environmental impact at the point where the energy is generated, especially if it’s from older, less efficient technologies. When paired with renewable energy sources like solar or wind power, heat pumps can operate almost entirely carbon-free, significantly reducing their overall environmental footprint.
Consistent Temperature Control
Heat pumps provide steady and even heating, maintaining a comfortable indoor environment without the temperature fluctuations often experienced with other systems, such as traditional gas furnaces or electric resistance heaters. This is because heat pumps constantly regulate and adjust the temperature, whereas gas furnaces and electric heaters tend to cycle on and off, leading to more pronounced temperature swings.
Long-Term Savings
Although the initial cost might be higher, the operational efficiency of heat pumps leads to long-term savings on energy bills. Over time, these savings can offset the initial investment. The payback period typically ranges from 5 to 10 years. This period can vary depending on factors such as local energy prices, climate, the efficiency of the specific model, and the amount of energy savings compared to your previous heating system.
Low Maintenance
Heat pumps generally require less maintenance than combustion-based heating systems. Regular filter changes and annual professional check-ups are typically sufficient to keep them running efficiently.
Safety
Without combustion, there’s no risk of carbon monoxide leaks, making heat pumps a safer option for home heating compared to gas furnaces or oil burners.
The Drawbacks of Home Heating with Heat Pumps
Initial Cost
The upfront cost of purchasing and installing a heat pump can range from $4,000 to $8,000, depending on the size and type of the unit. If modifications to your home’s ductwork are needed, this can add an additional $1,000 to $3,000 to the total cost. In contrast, the cost of installing a gas furnace typically ranges from $2,500 to $5,500. These figures are based on data available as of 2023 and can vary based on factors such as the specific model, installation complexity, and regional labor rates. For the most accurate and up-to-date pricing, it’s best to consult local HVAC professionals.
Efficiency in Cold Climates
Heat pumps are less effective in very cold climates, particularly when temperatures drop below 25 to 30 degrees Fahrenheit (-4 to -1 degrees Celsius). As temperatures fall into this range, their efficiency decreases significantly, and they may require a supplementary heating source, such as electric resistance heating, which can increase operating costs.
Electricity Dependency
Heat pumps run on electricity, so their efficiency and cost-effectiveness are closely tied to local electricity rates. In areas with high electricity costs, running a heat pump can become expensive.
Complex Installation
Installing a heat pump can be more complex and time-consuming compared to other heating systems. It often requires professional installation, which can add to the initial cost.
Noise
Some heat pump systems, particularly older models, can be noisy during operation, which might be a concern for some homeowners. The noise levels of these systems typically range from 40 to 60 decibels (dB). For comparison, 40 dB is about the noise level of a quiet library, while 60 dB is comparable to a normal conversation. In contrast, newer models are often designed to operate more quietly, with noise levels as low as 30 dB, making them much less intrusive.
Aesthetic Concerns
The outdoor unit of a heat pump system can be bulky and may not be visually appealing. It requires sufficient space and proper placement to ensure efficient operation and noise reduction.
Limited Lifespan in Harsh Conditions
In regions with extreme weather conditions, the lifespan of a heat pump might be shorter due to increased wear and tear. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure longevity and performance.
While heat pumps offer numerous benefits, it’s important to consider these drawbacks and assess whether a heat pump is the right choice for your specific needs and circumstances.
Understanding Gas Furnaces
How Gas Furnaces Work
Gas furnaces heat your home by burning natural gas. When the thermostat signals that heating is needed, a gas valve opens, and the furnace’s burners ignite the gas. The heat produced in the combustion chamber warms a heat exchanger, which then transfers this heat to the air. A blower fan circulates the warmed air through your home’s ductwork and into various rooms.
The combustion process produces exhaust gases, which are vented outside through a flue or chimney. Gas furnaces are particularly effective in cold climates due to their ability to produce a large amount of heat quickly and maintain it consistently. However, they do require a reliable natural gas supply and regular maintenance to ensure safety and efficiency.
The Benefits of Home Heating with Gas Furnaces
Powerful Heating
Gas furnaces are known for their ability to produce strong, consistent heat, making them an excellent choice for regions with extremely cold winters. They can quickly warm up your home and maintain a comfortable temperature even during the coldest months.
Cost-Effective Operation
In areas where natural gas is inexpensive, gas furnaces can be a very cost-effective heating solution. The cost per unit of heat generated is often lower compared to electric heating systems.
Reliability
Gas furnaces are highly reliable and can provide uninterrupted heating even during power outages, as long as the gas supply is unaffected. This is a significant advantage in regions prone to harsh winter storms.
Long Lifespan
With proper maintenance, gas furnaces can last 20 years or more, offering a durable and long-term heating solution for your home.
Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure
Many homes already have natural gas lines and ductwork in place, making the installation of a gas furnace relatively straightforward and less expensive compared to other heating systems.
Lower Initial Cost
The initial purchase and installation cost of a gas furnace is typically lower than that of a heat pump, especially if your home already has the necessary infrastructure.
Quick Heat Distribution
Gas furnaces can quickly distribute heat throughout your home, providing fast and efficient heating. This rapid response can be particularly beneficial in very cold weather.
The Drawbacks of Home Heating with Gas Furnaces
Environmental Impact
Gas furnaces burn fossil fuels, releasing carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the atmosphere. This contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and can have a negative impact on air quality and the environment.
Fluctuating Fuel Prices
The cost of natural gas can fluctuate based on market conditions, which can affect your heating bills. In some areas, natural gas prices can be volatile, leading to unpredictable heating costs.
Safety Concerns
Gas furnaces pose potential safety risks, including gas leaks and carbon monoxide poisoning. Proper installation, regular maintenance, and the use of carbon monoxide detectors are essential to mitigate these risks.
Maintenance Requirements
While gas furnaces are generally reliable, they require regular maintenance to ensure safe and efficient operation. This includes checking the burner, heat exchanger, and other components, as well as changing filters regularly.
Limited Cooling Capability
Unlike heat pumps, gas furnaces do not provide cooling. You’ll need a separate air conditioning system for cooling your home, which can add to the overall cost and complexity of your HVAC system.
Space Requirements
Gas furnaces require adequate space for installation and proper ventilation. This can be a concern in smaller homes or spaces where utility room is limited.
Dependence on Natural Gas Infrastructure
If your area does not have a reliable natural gas supply, or if you’re in a remote location, the cost and feasibility of installing a gas furnace may be prohibitive. Additionally, regions without natural gas infrastructure will need to consider alternative heating options.
Heat Pumps vs. Gas Furnaces – Highlights of Pros and Cons
| Criteria | Heat Pumps | Gas Furnaces |
| Efficiency | High efficiency, especially in mild climates | Efficient in cold climates |
| Environmental Impact | Lower environmental impact, no direct emissions | Burns fossil fuels, higher emissions |
| Operating Costs | Lower energy bills over time | Cost-effective where natural gas is cheap |
| Installation Costs | Can be higher but offset by long-term savings | Lower initial cost if infrastructure is present |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance requirements | Requires regular maintenance |
| Climate Suitability | Less effective in very cold climates | Ideal for very cold climates |
| Lifespan | Typically around 15 years | 20+ years with maintenance |
| Reliability | Consistent temperature control | Consistent and powerful heating |
| Safety | No risk of carbon monoxide leaks | Safety concerns with gas usage |
Things to Consider When Choosing Between Heat Pumps and Gas Furnaces
When deciding between a heat pump and a gas furnace for your home, several factors should be considered to ensure you make the best choice for your specific needs. Here’s a rundown of the key aspects to keep in mind:
Climate
The climate in your region is one of the most critical factors. Heat pumps are highly efficient in mild to moderate climates but can struggle in extremely cold conditions. In contrast, gas furnaces are well-suited for colder climates, providing reliable heat regardless of outdoor temperatures.
Initial Cost and Installation
Consider the initial cost of the system and the complexity of the installation. Heat pumps typically have a higher upfront cost and may require modifications to your existing ductwork or electrical system. Gas furnaces usually have a lower initial cost, especially if your home already has a natural gas line and suitable ductwork.
Operating Costs
Operating costs can vary based on local energy prices. Heat pumps run on electricity, so their cost-effectiveness depends on your local electricity rates. Gas furnaces depend on natural gas prices, which can fluctuate. It’s essential to compare the long-term operating costs of both systems in your area.
Energy Efficiency
Evaluate the energy efficiency of each system. Heat pumps are generally more efficient because they transfer heat rather than generate it. However, their efficiency decreases in very cold weather. Gas furnaces are highly efficient in converting fuel to heat, especially modern models with high AFUE ratings.
Environmental Impact
Consider the environmental impact of each system. Heat pumps use electricity and can be paired with renewable energy sources, making them a greener option. Gas furnaces burn natural gas, which produces carbon emissions. If reducing your carbon footprint is a priority, a heat pump might be the better choice.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Think about the maintenance requirements and expected lifespan of the systems. Heat pumps generally require less maintenance and have fewer components that can fail. Gas furnaces need regular maintenance, including inspections and cleaning of the burners and heat exchanger. Both systems can have long lifespans, but proper maintenance is crucial.
Home Infrastructure
Assess your home’s existing infrastructure. If your home already has a natural gas line and ductwork, installing a gas furnace might be simpler and less expensive. If you don’t have a gas line, the cost of installation can be significant. Heat pumps might require upgrades to your electrical system and space for the outdoor unit.
Comfort Preferences
Consider your comfort preferences. Heat pumps provide consistent and even heating, while gas furnaces can quickly warm up your home and maintain high temperatures. Think about how each system will affect your indoor comfort throughout the year.
Availability of Fuel Sources
The availability and reliability of fuel sources in your area can influence your decision. If you live in an area with frequent power outages, a gas furnace might be more reliable since it doesn’t rely on electricity. Conversely, if natural gas supply is limited or costly, a heat pump might be more practical.
Conclusion
When it comes to the decision of heat pumps vs. gas furnaces, it’s essential to consider various factors unique to your home and location. Both systems have their strengths and limitations, so it’s crucial to assess your specific heating requirements, climate conditions, and long-term energy costs. By carefully evaluating these aspects, you can choose a heating system that offers optimal comfort, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for your home.
More Articles About Home Heating

Tips and Tricks on How To Remove Bad Smell From The Air Ducts
The bad smell from the air ducts of your HVAC system is a common problem for many homeowners. Ductwork is the…

Heat Pump Not Cooling? Here’s What You Need to Know
Heat pumps are essential not only in the winter for heating our homes but also in the summer to cool…

Compare Ductless Mini-Split Heat Pumps vs. Window Heat Pumps: Which Is Right for You?
In this article, we are going to look at ductless mini-split heat pumps vs. window heat pumps, examine how each…