Compare Heat Pumps vs. Wood Stoves: Find the Best Solution for Your Home Heating
When it comes to keeping your home warm and cozy, compare heat pumps vs. wood stoves to see which one fits your needs best.
Choosing the right heating system is crucial for comfort and cost-efficiency. In this article, we’ll explore the pros and cons of both systems to help you make an informed decision. Learn about how each system works, their unique benefits, and potential drawbacks.
Whether you’re drawn to the modern technology of heat pumps or the classic charm of wood stoves, we’ve got you covered. Let’s find the perfect heating solution for your home and lifestyle.
Why Compare Heat Pumps vs. Wood Stoves?
This article isn’t about finding the most efficient heating system or picking the best brand or model.
Instead, it provides essential information about two popular home heating systems: heat pumps and wood-burning stoves.
During the winter months, energy usage and your utility bills can increase significantly. That’s why it’s crucial to choose the right type of heating system, the right device, and a reliable fuel supply.
With today’s high energy prices and the lack of natural gas in some areas, heating with electricity or wood can save you money and keep you comfortable. Plus, if you choose an energy-efficient and eco-friendly model, you can keep your energy costs and gas emissions in check.
We compared heat pumps vs. wood stoves to help you decide between the advanced, modern technology of heat pumps and the traditional, reliable heating of wood stoves with their proven track record.
What Are Heat Pumps and Why Should You Buy One?

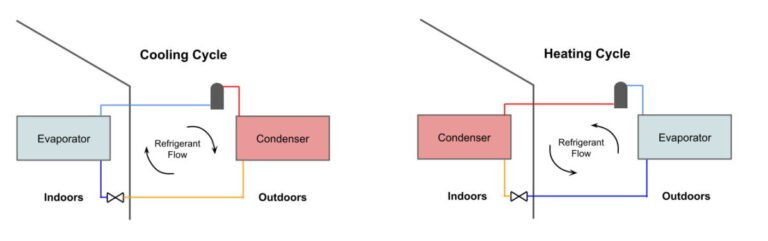
Heat pumps are electrical devices that capture heat and move it from one place to another. Unlike other heating devices, such as furnaces, they don’t generate heat.
There are several types of heat pumps designed to heat homes with the highest energy efficiency among all electric options.
Homeowners can choose between two main types: air-source and geothermal systems.
Air-source heat pumps capture heat from the surrounding air, while geothermal systems extract heat from the ground or a body of water.
During winter, heat pumps bring heat from the outdoors into your home. In summer, they work in reverse, removing heat from your home and releasing it outside.
According to some manufacturers, heat pumps can produce up to four times as much energy as they consume. This efficiency is their main strength but there are also other benefits.
Advantages of Heat Pumps
- High efficiency: Heat pumps can be up to four times more energy-efficient than electric and gas condensing models, which max out at 99% efficiency.
- Complete HVAC solution: They not only heat homes but also provide cooling and dehumidification, keeping your home comfortable year-round. They offer consistent heating without temperature fluctuations.
- Whole-house climate control: Using a ductwork system, these units deliver heat throughout the house. When properly sized and installed, they ensure every room is evenly heated and centrally controlled. Programmable and smart thermostats enhance control and monitoring, improving both comfort and energy usage.
- Air quality: They improve air quality by controlling humidity and using built-in filters to clean the air. They don’t dry out the air when heating and effectively remove excess moisture during summer.
- Environmentally friendly: Since heat pumps run on electricity, they don’t burn fossil fuels directly. However, the environmental impact depends on how the electricity is generated. If it comes from coal or nuclear energy, the solution is less eco-friendly.
- Long-lasting: Properly installed and maintained systems, especially geothermal ones, can last over 50 years.
- Low maintenance: These units require only basic maintenance to operate efficiently and last long.
- Safe: They don’t burn gases or produce harmful emissions like carbon monoxide, making them safe for your family and the environment.
- Better savings: In areas with moderate climates, they can pay for themselves in a few years. Homeowners can also benefit from rebates and federal/state tax credits when purchasing these systems.
Disadvantages
- The initial investment can be higher than for other heating systems.
- Professional installation is required.
- Energy efficiency decreases as the temperature drops. In cold weather, the efficiency is lower, so supplemental heating might be necessary.
- Heat pumps don’t produce intense heat, which might be uncomfortable for some, especially in cold winters and if the house is not adequately insulated.
- They cannot operate during power outages.
What Are Wood Stoves and Why Should I Buy One?

While wood-burning stoves are mostly built to heat one or two rooms, some models include blowers and other features that can help heat your entire house.
They are efficient, and if you have your own wood supply or can get wood at a lower price, even better. Note that the quality of the fire depends on the type of wood you burn and its moisture content.
When burning wood, these stoves generate heat and release gases into the atmosphere. While many argue that wood stoves pollute the planet, the truth is they are carbon neutral.
This means they produce gases that are not harmful. If you own a model that meets or exceeds clean air standards, you are in good shape.
Advantages of wood stoves
- High efficiency: Modern and advanced wood stoves can achieve around 70-80% efficiency. This makes them a cost-effective option for heating your home.
- Renewable resource: Wood is a renewable resource. By using wood, you are tapping into a sustainable energy source.
- Reliable operation: Wood stoves operate even during power outages, making them very reliable. You can stay warm even when the electricity goes out.
- Longevity: Wood stoves can last a long time since they don’t use moving parts or electricity. Their durable construction ensures years of use with minimal wear and tear.
- Versatility: Besides heating, wood stoves can also be used for cooking. This dual functionality can be particularly useful during emergencies.
Disadvantages
- Slow to heat: It takes longer to light the fire and heat the room. Patience and preparation are needed to get the stove going.
- Air pollution: Wood stoves are not as clean as heat pumps; they produce smoke and soot, which can significantly contribute to air pollution, especially when the wood is not completely burned. Poor air quality can affect your health and the environment.
- Fire hazard: Creosote, a by-product of combustion, can cause chimney fires. Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to prevent this risk.
- Inconvenience: They are not as convenient as pressing a button on electric devices. Before the wood stove starts heating your home, you must often arrange wood delivery, split the logs, and bring the wood inside the house. Additionally, you will have to remove and dispose of ash. This process requires time and effort, which may not be suitable for everyone.
- Limited function: Wood stoves provide only heating. You’ll need a separate system for cooling your home in the summer.
- Safety concerns: They are not as safe as heat pumps. Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial to ensure safe operation.
- Maintenance: Wood stoves require constant care. Someone must always be at home to manage the fire and handle cleaning. This ongoing responsibility can be a burden for busy households.
- Urban limitations: They are difficult to use in urban areas, especially in apartments. Limited space and building regulations can restrict the use of wood stoves in these environments.
Things to Consider When Comparing Heat Pumps vs. Wood Stoves
Emission and Environmental Impact
Since heat pumps are powered by electricity, they do not emit pollutants directly. However, they can contribute to pollution if the electricity comes from “dirty” sources like coal, oil, or nuclear energy. On the other hand, electricity generated from renewable sources such as wind, solar, and hydro is clean and doesn’t impact the climate or air quality.
When wood stoves are burning, they release pollutants, which can contribute to environmental hazards such as smog and acid rain. The impact depends on the type and quality of the wood, how it’s stored, whether it burns completely, and whether the stove is EPA-certified. Despite this, wood is a carbon-neutral energy source, releasing the same amount of carbon dioxide during burning as it absorbed during its life cycle.
Efficiency
Heat pumps operate on a different principle than other heating systems; they move heat rather than generate it, which allows them to produce heat with over 100% efficiency. Some manufacturers claim efficiency levels up to four times higher than conventional heating systems. While they can function in various climates, heat pumps are most effective in mild climates.
Wood-burning stoves are also efficient. Wood is an affordable and renewable heat source, costing less than burning natural gas or using electricity. Traditional fireplaces are only 10-20% efficient, with most of the heat escaping up the chimney. However, modern wood stoves can achieve efficiencies of approximately 80-85%, similar to an average gas furnace. EPA-certified wood stoves can offer even higher efficiency, especially those with innovative features like catalytic converters.
Note: There are two types of efficiencies related to wood stoves: combustion efficiency (how well the stove converts wood into usable heat) and overall efficiency (how much heat is transferred to the space). Advertisements often highlight the higher combustion efficiency, but the overall efficiency is what truly matters. For accurate information on specific models, check the EPA certified wood stove database.
Ease of Use
Electric heat pumps are very easy to operate and monitor. You simply press a button, and it works. Even better, you can use a smart or programmable thermostat to schedule when it turns on and off.
Wood stoves, on the other hand, require more effort. You need to have firewood delivered and split into the recommended size. Once the wood is burning and ash accumulates, you’ll need to clean and dispose of the residues. Additionally, about once a year, you should call a professional to inspect and clean the chimney to ensure proper draft and remove creosote deposits, which can cause chimney fires.
Comparing Costs
According to homeadvisor.com, heat pumps might cost you between $4,000 and $7,000, depending on the type and size. The most expensive type is geothermal (over $10,000), while split systems cost much less.
The average price range for wood stove installation is between $1,200 and $4,500, and if a chimney is installed up to $7,000.
So, Which Is Better: A Heat Pump or a Wood-Burning Stove?
Homeowners today have numerous options for heating their homes: gas, oil, electricity, wood, solar, or a combination. However, not all systems are equally cost-effective, efficient, or environmentally friendly.
Choosing the best option can be overwhelming.
That’s why we’ve compared two popular home heating systems—heat pumps vs. wood stoves. Heat pumps offer advanced technology, while wood-burning stoves provide traditional, proven methods.
If you enjoy lighting your own fire, the smell of wood, and the sight and sound of crackling logs, a wood stove might be perfect for you. On the other hand, if you prefer modern technology, have a flexible budget, and appreciate the convenience of everything working at the push of a button, a heat pump could be your best choice.
More About Heat Pumps

Heat Pump Not Cooling? Here’s What You Need to Know
Heat pumps are essential not only in the winter for heating our homes but also in the summer to cool…

Compare Ductless Mini-Split Heat Pumps vs. Window Heat Pumps: Which Is Right for You?
In this article, we are going to look at ductless mini-split heat pumps vs. window heat pumps, examine how each…

Explore the Differences: How Ductless vs. Ducted Heat Pumps Compare
Deciding between ductless vs. ducted heat pumps is as easy as planning a holiday. You know it’s going to cost…