What Are Gas-Powered Heat Pumps? Are They the Better Choice?
Are you exploring more efficient and cost-effective solutions for heating and cooling your home?
Consider the potential of gas-powered heat pumps!
These innovative systems provide an excellent alternative to traditional methods, leveraging gas to power the heat exchange process. This not only enhances efficiency but also keeps running costs low, especially in regions with high electricity rates or unstable power supplies.
In this overview, we discuss the advantages and disadvantages of gas-fired heat pumps and provide a comparative analysis against their electric counterparts.
What Are Gas-Powered Heat Pumps?
Gas-powered heat pumps are advanced heating and cooling systems that use natural gas as their primary energy source, rather than electricity. This type of system falls under the category of absorption heat pumps, which also includes systems powered by propane, solar, or geothermal heated water.
However, because natural gas is the most commonly used energy source among them, they are specifically referred to as gas-fired heat pumps.
These systems are a great fit for today’s larger homes, stepping up where traditional electric heat pumps might fall short.
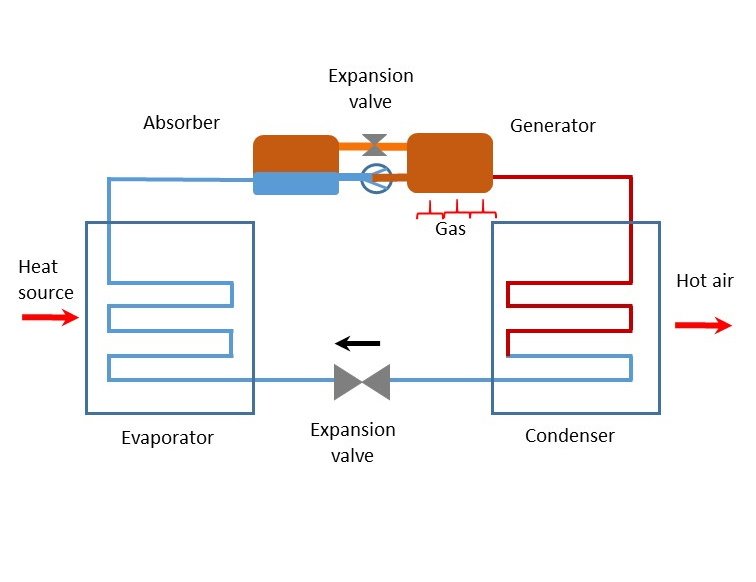
How a Gas-Powered Heat Pump Works
A gas-powered heat pump uses a clever device called a thermal compressor, which combines a generator and an absorber, to replace the typical electric compressor found in most heating and cooling systems. This setup not only makes the system more efficient but also reduces running costs because it uses natural gas instead of electricity.
Here’s how it works: The generator heats a mixture of ammonia and water, causing the ammonia to turn into vapor while leaving behind a weaker solution. This ammonia vapor then moves to the condenser, where it cools down and releases heat into the room, turning back into a liquid but still under high pressure.
This high-pressure liquid ammonia then passes through an expansion valve into the evaporator, where it rapidly cools and evaporates, absorbing heat from the air. This cooled air is what you feel blowing from your air conditioner.
Finally, the ammonia vapor returns to the absorber, mixes back into the weak solution, and the whole cycle starts over.
Some systems also include a special feature called a Gas Absorption eXchange (GAX) heat exchanger, which captures extra heat from the process to boost efficiency even further.
Advantages of Gas-Fired Heat Pumps
- Optimized for Large Residences: Natural gas heat pumps are particularly effective in properties exceeding 4,000 square feet, delivering robust heating and cooling capabilities without compromise.
- Zoned Comfort Solutions: They enable precise temperature control in different areas of your home, allowing for customized comfort and enhanced energy efficiency across various living spaces.
- Environmentally Conscious Refrigeration: By using natural ammonia instead of synthetic refrigerants that deplete the ozone, the gas-fired heat pumps represent a greener option for residential heating and cooling.
- Versatile Energy Compatibility: Designed to operate with multiple energy sources, including natural gas, solar energy, and geothermal hot water, these pumps offer flexibility in how they can be powered, depending on your local resources and preferences.
- Reduced Emissions: Compared to traditional heating systems like gas or coal furnaces, gas-fired heat pumps emit fewer pollutants, supporting a cleaner environment while efficiently managing your home’s temperature.
- Consistent Year-Round Performance: Unlike electric heat pumps, which may struggle in extreme temperatures, gas-fired pumps maintain high efficiency and performance throughout the year, even in the face of harsh weather conditions.
- Dependable Operation in Power Outages: Their ability to operate independently of the electrical grid ensures that your home remains heated or cooled even during power interruptions, providing unmatched reliability.
- Efficient Heating in Cold Climates: These systems are capable of extracting ambient heat from cold environments effectively, making them particularly useful in regions that experience severe winters.
- Superior Efficiency Across Climates: Generally, gas-powered heat pumps are acknowledged for their higher efficiency over a broad spectrum of climatic conditions, offering significant energy savings and operational cost reductions.
- High Coefficient of Performance (COP): With a higher COP rating, these units are recognized for superior operational efficiency, translating to better energy utilization and lower utility bills over time.
Drawbacks
- Initial and Operational Costs: Although gas-powered heat pumps have higher purchase, installation, and operational costs compared to other systems, their efficiency across various seasons—especially in extreme climates—can offset these initial investments. In areas with very cold or hot and humid conditions, these units maintain high efficiency, potentially leading to long-term savings.
- Fuel Cost Considerations: Typically, these systems use natural gas, which tends to be more expensive than electricity, in some areas. This factor can influence overall running costs and should be considered when evaluating the economic feasibility of installing a gas heat pump.
- Safety Measures: Like any gas appliance, there is a risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. It’s crucial to have a reliable carbon monoxide detection system installed on your property to ensure safety and peace of mind.
Gas Heat Pumps in Extreme Climates
It is worth noting that gas heat pumps excel in extreme climates where electric systems often struggle.
The electric units can find it difficult to deliver adequate heating, especially in frigid conditions, because their performance is heavily dependent on weather conditions, which are unpredictable.
Often, they must work excessively hard to maintain efficiency, which leads to higher power costs and greater wear on the equipment. This increased strain complicates maintenance and can potentially shorten the system’s lifespan.
Gas-fired units, on the other hand, shine under these challenging circumstances. When temperatures plummet and warmer air becomes scarce, gas-fired heat pumps continue to operate effectively.
Useful Tips for Homeowners
- Assess Energy Sources: Before anything else, check if natural gas is readily available and affordably priced in your area. It’s a key factor because your gas-powered heat pump will need it to function.
- Evaluate Efficiency Ratings: Keep an eye out for units with top-notch efficiency ratings. Look for a high Coefficient of Performance (COP) and Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER). These figures tell you how well the unit uses gas to heat or cool your place.
- Size Appropriately: Getting the right size for your heat pump is crucial. If it’s too big or too small, it won’t be as efficient, could wear out faster, and might hike up your energy bills. It might be wise to get a professional to size it perfectly for your home.
- Check for Noise Levels: Gas-powered heat pumps tend to be louder than electric ones. It’s a good idea to check the decibel levels to ensure it won’t disrupt your home environment. Think about where you’ll place it too.
- Research the Brand and Model: Choose a brand with a solid reputation for reliability and good customer service. Dive into reviews and consumer feedback, especially those focusing on gas-powered models, to see what actual users say.
- Understand the Warranty: Take a close look at the warranty terms. A longer warranty on key parts like the gas engine and compressor can really give you extra security.
- Consider Maintenance Needs: Gas-powered heat pumps usually require more frequent maintenance than electric ones, especially around the gas engine. Make sure you’re up for the upkeep.
- Local Climate Suitability: Make sure the pump is a good fit for your area’s climate. Gas-powered models are typically strong performers in cold weather, but always double-check this with the specs to avoid surprises.
- Look for Rebates and Incentives: Do some digging into any local or federal incentives that might help lower the costs of buying and installing your heat pump. These can significantly reduce your initial expenses.
- Consult with Professionals: Talk to HVAC pros who know their way around gas-powered heat pumps.
So, Are Gas-Powered Heat Pumps the Right Choice?
Gas-powered heat pumps are an exceptional choice, especially for larger homes. They offer superior efficiency in heating and cooling expansive areas and feature zone control, which allows for customized temperature settings throughout the home. Although the initial purchase, installation, and operational costs of a gas heat pump are higher, the capability to maintain a comfortable living environment year-round, regardless of extreme weather conditions, can justify the investment.
For those living in average-sized homes in moderate climates, a standard electric air source heat pump will likely meet your heating and cooling needs efficiently and cost-effectively. However, if you require more robust climate control capabilities, a natural gas-fired heat pump could be the ideal solution.
More About Heat Pumps

Heat Pump Not Cooling? Here’s What You Need to Know
Heat pumps are essential not only in the winter for heating our homes but also in the summer to cool…

Compare Ductless Mini-Split Heat Pumps vs. Window Heat Pumps: Which Is Right for You?
In this article, we are going to look at ductless mini-split heat pumps vs. window heat pumps, examine how each…

Explore the Differences: How Ductless vs. Ducted Heat Pumps Compare
Deciding between ductless vs. ducted heat pumps is as easy as planning a holiday. You know it’s going to cost…






